Articles 324 to 329 in Part XV of the Constitution deals with the Electoral System of India. Article 324 of the Constitution provides for an independent Election Commission in order to ensure free and fair elections in the country.

Parliamentary General Elections (Lok Sabha)
The citizens of age 18 and above in the country elect the members of the Lok Sabha through direct voting. Each state is divided into territorial constituencies for the purpose of elections. One member of Lok Sabha is elected from each constituency.
A candidate who is elected serves for five years. They are known as Members of Parliament. A total of 543 Lok Sabha members are chosen. Unless dissolved, the Lok Sabha continues to function for five years from the date of its first meeting. The next Lok Sabha elections in India will be held in 2024.
Rajya Sabha Elections
Rajya Sabha has a process of indirect elections where the State assemblies select members as per the proportion of seats available. The seats in Rajya sabha are allocated according to the proportion of the population. Uttar Pradesh has the largest population, and it has the most seats allocated in Rajya sabha. In contrast, states like Nagaland and Mizoram are sparsely populated and have one seat. Rajya Sabha can never be dissolved, and the members are elected for six years.
State Assembly Elections (Vidhan Sabha)
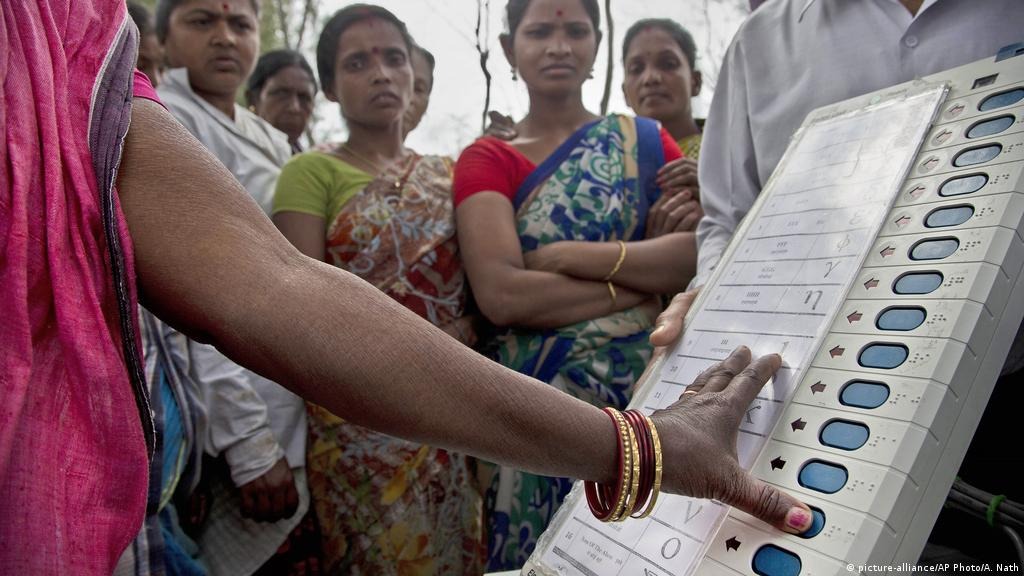

Assembly election is the election for the state legislative assembly. Each state is divided into territorial constituencies for the purpose of elections. One member of the legislative assembly is elected from each constituency through direct voting. The elected members are called MLAs. The leader of the winning party becomes the chief minister of that state.
The maximum number of members of the legislative assembly is 500, and the minimum strength is 60. A candidate who gets elected holds their seat for five years. Currently, Himachal Pradesh and Gujarat are going to vote for State Assembly Elections.
Zila Panchayat Elections
Zila Parishad is the third tier of the Panchayati Raj system which administrates at the District level. The Zilla Parishad is a link between the State government and the Gram Panchayats. It is headed by a President who is elected directly from among the elected members of Zila panchayats of various districts. Each member of Zila Panchayat in different districts is elected directly by the citizens of age 18 and above. Each District (Zila) is divided into Gram Panchayats which are headed by a Pradhan or Mukhiya or Sarpanch elected directly by the citizens of that village. Currently, Haryana is under polls for panchayat elections.
Urban Municipal Elections
Municipal Corporation Elections (India) are conducted to elect municipal councilors and ward representatives for Municipal Corporations in urban regions. The town is divided into wards according to its population, and representatives are elected from each ward. The members elect a president among themselves to preside over and conduct meetings. The Councillors or Ward Members are chosen by direct election from electoral wards in the Nagar Panchayats. Delhi will go under polls for municipal elections in December.
By Elections
A by-election or bypolls is an election used to fill an office that has become vacant between general elections. The seat could become vacant due to reasons like if a member of Parliament resigns, dies, switches parties, or if the candidate wins from both constituencies, they have to vacate one of the seats. A by-election is only open to voters of that particular constituency only who directly vote to elect the new member. Recently, Adampur, Munugode, Dhamnagar, Gopalganj, Mokama, Andheri West, and Gola Gokranath concluded their bypolls.